Breast imaging understanding how accuracy is measured when lesions are the unit of analysis review
Breast imaging understanding how accuracy is measured when lesions are the unit of analysis review
Info
- Breast imaging: understanding how accuracy is measured when lesions are the unit of analysis. Breast J. Nov-Dec 2012;18(6):557-63. doi: 10.1111/tbj.12009.
Introduction
- Breast Cancer Patients에서
- multiple lesions이 있거나 알려진 primary tumor 외의 다른 abnormal area를 찾는 경우가 있음
- e.g, Cancer 관리를 위한 mammography 이후 추가 imaging 촬영, MRI로 수술전 계획(Preoperative planning)을 세우거나 staging of disease를 정하는 것 등
- 이 경우, Radiologists가
- location of additional lesions을 정확히 찾고 이 lesions이 significant한 지 올바르게 판정하는 것이 중요함
- Significant: lesion이 malignant하거나 treatment planning을 세워야 할 정도로 malignant로 발전할 가능성이 큼(high potential)을 의미
- multiple lesions이 있거나 알려진 primary tumor 외의 다른 abnormal area를 찾는 경우가 있음
- Lesion as the unit of analysis
- 위의 경우, lesion level analysis가 필요함
- 일반적인 SN, SP, ROC curve estimates의 사용은 한계가 있음
- Purpose of the study
- 환자가 위치를 정확히 알아야 하는 multiple lesion이 있을 경우의 lesion level analysis에 대해 다룸
- lesion이 unit of analysis일 때는 일반적으로 사용하는(usual estimate) specificity나 ROC curve 사용이 어려움을 설명하고자 함
Materials and Methods
Illustrative Example
- FDG PEM(F18-2-fluoro-2-deoxy-D-glucose positron emission) MMG study
- objective: FDG PEM의 accuracy 평가
- subjects: women newly diagnosed with breast cancer(invasive or in situ)
- MRI image와 FDG PEM image를 비교
- 유방절제술(mastectomy)의 pathology information이 reference standard
Illustrative Figure
- 10 patients as an example
- it is not meant to reflect the true accuracy of any imaging test
- 9 women with significant disease, one woman without breast cancer
- 17 significant lesions (10 true positives, 7 false negatives)
- 3 false-positive findings
Methods of Analysis
- Sensitivity of a test
- the probability that the test indicates disease is present given that disease is truly present
- \[SN = P(Test + | Disease)\]
- Specificity of a test
- the probability that the test indicates there is no disease given that disease is truly absent
- \[SP = P(Test - | No Disease)\]
- Unit of Analysis가 무엇인지 중요함
Results
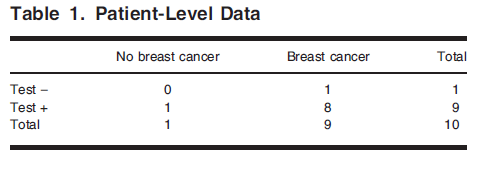
Patient-Level Analysis
- Typical way of evaluating the accuracy of a medical test
- Goal
- 질병이 있는 사람들과 없는 사람들을 test가 얼마나 잘 탐지(detect)하는 지를 평가함
2 by 2 table
- \[SN = P(Test + | Disease) = \frac{P(Test + \& Disease)}{P(Disease)} = \frac{(8/10)}{(9/10)} = 8/9 = 89%\]
- \[SP = P(Test -| No\ disease) = \frac{P(Test - \& No\ disease)}{P(No\ disease)} = \frac{(0/10)}{(1/10)} = 0%\]
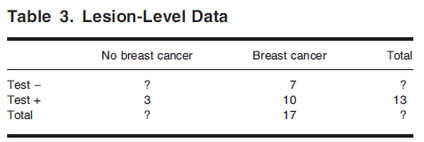
Breast-Level Analysis
- The breast as the unit of analysis
- 이 경우, patient level analysis에 비해 n수가 2배가 됨(each breast에 대해 평가)
- 2 by 2 Table
- \[SN = P(Test + | Disease) = \frac{P(Test + \& Disease)}{P(Disease)} = \frac{(8/20)}{(10/20)} = 8/10 = 80%\]
- \[SP = P(Test -| No\ disease) = \frac{P(Test - \& No\ disease)}{P(No\ disease)} = \frac{(9/20)}{(10/20)} = 90%\]
- Patient level analysis의 SP 0%가 Breast level에서는 90%가 됨
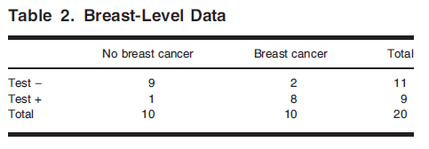
Lesion-Level Analysis
- The lesion as the unit of analysis
- Figure 1에서 20 regions이 areas of interest였음
2 by 2 Table
- Lesion level에서는 True Negative를 정의할 수 없음
- Radiologist가 식별하지 않고 또 Pathology에서도 암이 없다고 나온 lesion을 어떻게 ‘True Negative’하다고 lesion level에서 정의할 수 있을지?
- “True Negative”라고 lesion level에서 정의할 수 있을 영역의 경우의 수가 너무 많기 때문에 위 table의 물음표(?)를 채울 명확한 방법이 없음
- (There are infinitely many possibilities for defining areas that could be marked as true negatives. The end result is that we have no obvious way to fill in this cell)
- “True Negative”라고 lesion level에서 정의할 수 있을 영역의 경우의 수가 너무 많기 때문에 위 table의 물음표(?)를 채울 명확한 방법이 없음
- 따라서 Lesion level에서는 Specificity 계산을 할 수 없음 (민감도는 가능함)
- Radiologist가 식별하지 않고 또 Pathology에서도 암이 없다고 나온 lesion을 어떻게 ‘True Negative’하다고 lesion level에서 정의할 수 있을지?
- \[SN = P(Test + | Disease) = \frac{P(Test + \& Disease)}{P(Disease)} = 10/17 = 59%\]
Receiver Operating Characteristic (ROC) Curve Analysis
- Empirical ROC curve
- data are first ranked by the test result (값이 높을수록 질병이 있을 확률이 큼)
- the values above that threshold are considered positive
- For each threshold, SN and SP is calculated
- ROC Curve is the plot of SN by 1 - SP
- Lesion level에서 SP 계산을 할 수 없으므로 ROC curve도 estimate 할 수 없음
Discussion
- 예시에서 Pathology information이 available 했음
- all women in our example had a bilateral mastectomy
- breast or lesion level 평가를 위해서는 confirmed case only 등으로 study design을 조정해야함
- 한 환자가 Multiple lesions이 있는 경우
- Patient level 또는 Breast level에서는 적절히 평가할 수 없음
- the location of the lesions의 평가 또한 patient/breast level에선 고려하지 않음
- Correctly locate a lesion에 대한 test의 accuracy 평가
- LROC (Localization ROC)
- only single lesion에 대해 평가
- FROC (Free Response ROC)
- Observation은 mark-rating pairs의 형태
- Mark: location identified by a radiologist as appearing suspicious of disease
- Rating: the assessment of the probability disease is present at that location
- the fraction of identified locations that are cancerous lesions by the fraction of the identified locations that are not의 plot임
- the average number of false-positives per patient(FPP)
- Lesion level sensitivity와 함께 FPP를 보고
- Proportion of patients who have any false-positive finding도 함께 보고
- Lesion level sensitivity와 함께 FPP를 보고
- the Poisson model for the number of false positives
- the number of FPs 가 Poisson distribution을 따른다고 가정하고 Patient level에서의 Specificity를 추정함(the probability of no false-positive findings in a patient 추정에 Poisson 분포를 적용)
- The lesion-level sensitivity와 patient level specificity에 대한 joint modeling을 random effects model로 설정할 수도 있음(by Zwinderman et al.)
- LROC (Localization ROC)
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.